Title: Achieving Magnetic Refrigerants with Large Magnetic Entropy Changes and Low Magnetic Ordering Temperatures
Authors: Qiao-Fei Xu, Man-Ting Chen, Ruo-Tong Wu, La-Sheng Long*, Lan-Sun Zheng
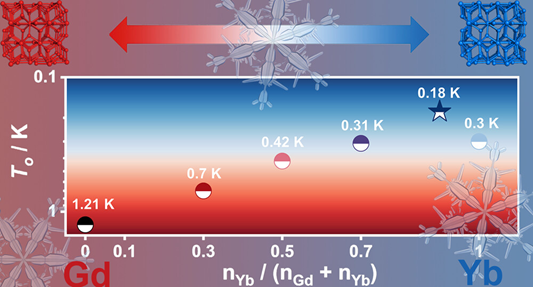
Abstract: Adiabatic demagnetization refrigeration (ADR) is a promising cooling technology with high efficiency and exceptional stability in achieving ultralow temperatures, playing an indispensable role at the forefront of fundamental and applied science. However, a significant challenge for ADR is that existing magnetic refrigerants struggle to concurrently achieve low magnetic ordering temperatures (T0) and substantial magnetic entropy changes (−ΔSm) at ultralow temperatures. In this work, we propose the combination of Gd3+ and Yb3+ to effectively regulate both −ΔSm and T0 in ultralow temperatures. Notably, the −ΔSm values for Gd0.1Yb0.9F3 (1) and Gd0.3Yb0.7F3 (2) in the 0.4–1.0 K range exceed those of all previously reported magnetic refrigerants within this temperature interval, positioning them as the most efficient magnetic refrigerants for the third stage to date. Although the −ΔSm values for Gd0.5Yb0.5F3 (3) in 1–4 K are less than those of the leading magnetic refrigerant Gd(OH)F2, the −ΔSm values for Gd0.7Yb0.3F3 (4) in 1–4 K at 2 T surpass those of all magnetic refrigerants previously documented within the same temperature range, making it the superior magnetic refrigerant for the fourth stage identified thus far.
Full-Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.4c04258