学术讲座
题 目: Molecular Functions of Surface Nano-Network Films based on Rod-shaped Ru Complexes on ITO Electrode
讲座人: Prof. Masa-aki Haga
Department of Applied Chemistry,
Faculty of Science and Engineering, Chuo University(日本中央大学)
时 间: 6月20日(周四)10:00-12:00
地 点: 卢嘉锡楼202报告厅
摘要:
Functional surfaces are one of the important research targets in various fields. In order to adopt the function on a surface, metal complex is an important candidate for a surface modifier.1)2) In particular, redox-active metal complexes on the electrode surface have paid much attention because of many applications for molecular devices,3) catalysis, and energy-storage 4) or -conversion.
We have developed the surface nano-network structures on an solid electrode by using a coordination layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly of rod-shaped complexes as a linker unit, which was fabricated by the repeatedly alternating immersion method on an ITO electrode. Figure 1 shows three illustrative examples of surface LbL structures based on rod-shaped Ru complex with phosphonate groups at both ends, which reveals the following functions:
(1) Scalable assembly of homo-layered LbL films in Figure 1(a) were grown on the ITO electrode, in which the smaller dependence of the ET rate on the film thickness was observed. The stepping-stone mechanism plays an important role for the ET events in the film.5) In the homo-layer films, the movement of counter anion on the charging-discharging process were applied to the redox capacitor for an energy storage device.4) 6)
(2) Heterolayer films composed of two Ru complex units with different redox potentials in Figure 1(b) was constructed. The potential gradient in the heterolayer film exhibited an electrochemical rectification, which led to the stabilization of the charge trapped state. The resulting two states showed the opposite direction of the photocurrent under the photoirradiation. Therefore, the present heterolayer films can be applied to the photo-responsive memory device. 7)
(3) Electrochemical interfacing of Prussian blue (PB) on the Ru complex having phosphonate groups was observed (see Figure 1(c)). As for the ITO||(Ru complex)/(PB nanocrystal) heterolayer films, interesting ion transport gating of PB MOF nanocrystals was observed by EQCM measurements.8)
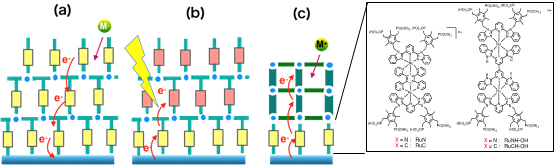
Figure 1. Illustrative examples of surface coordination LbL nano-network structures: (a) homo film, (b) hetero film under photoirradiation, (c) heterojunction composed of molecular layer/ PB MOF nanocrystals on the electrode, and chemical structures of two rod-shaped dinuclear Ru complexes.
References:
1. K. Kobayashi, N. Tonegawa, J. Hikida, M. Haga, et al., Langmuir , 24, 13203 - 13211(2008).
2. M. Haga, K. Kobayashi, and K. Terada,Coord. Chem. Rev., 251, 2688 – 2701 (2007).
3. H. Atesci, V. Kaliginedi, H. Ozawa, M. Haga, S. J. Molen et al., Nat. Nanotech., 2018, 13, 117.
4. V. Kaliginedi, H. Ozawa, K. M. Fromm, M. Haga, et al, Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 17685.
5. K. Terada, H. Nakamura, K. Kanaizuka, M. Haga, Y. Asai, and T. Ishida, ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 1988.
6. K. Yoshikawa, D. Motoyama, and M. Haga, et. al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 26990.
7. T. Nagashima, T. Nakabayashi, M. Haga, et al, Chem. Eur. J., 2016, 22, 1658.
H. Sato, M. Ide, M. Kurihara, H. Nishihara, M. Haga, manuscript in preparation (2019).
